DRIVING AN EV
USEFUL TIPS FOR NEW EV DRIVERS

MAIN DIFFERENCES
BETWEEN DRIVING AN EV AND AN ICE VEHICLE
REGENERATIVE BRAKING
Traditional brakes use friction to stop a vehicle, generating heat energy that is often wasted. Engineers have adapted a method from electric trains to recycle some of this energy back into the vehicle’s battery. While many conventional vehicles use regenerative braking, it serves as the primary system in electric vehicles, with hydraulic brakes as a backup, enhancing energy efficiency and driving range.
Regenerative brakes use an electric motor instead of traditional discs to slow the vehicle. These in-wheel motors capture energy from forward motion during deceleration and redirect it to the battery for acceleration.
INSTANT TORQUE
Instant torque enables faster acceleration in electric vehicles. Electric motors provide maximum torque immediately, offering quick, responsive power unlike the gradual acceleration and gear shifts found in traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
LOW NOISE/VIBRATION
EVs are almost silent when driving. The electric motor produces little to no noise, and there are no vibrations from a running engine. To ensure safety, many EVs include artificial noisemakers to alert pedestrians.
HANDLING
EVs have a lower centre of gravity due to their low-mounted batteries, making them feel more stable and balanced when cornering. However, the added weight can impact handling during sharp turns or aggressive driving.
NO CONGESTION CHARGE
Renting an electric vehicle (EV) exempts you from the London congestion charge until December 2025. This makes city travel more economical and eco-friendly, helping you save on fees while supporting cleaner air in the capital.
ROUTE PLANNING
HOW TO DO IT EFFICIENTLY

DON’T LEAVE CHARGING TO CHANCE
It’s crucial to map out your charging points in advance. Researching and identifying charging stations along your route will help you determine when and where to recharge, significantly reducing range anxiety.
Taking breaks is essential, so stretch your legs and recharge yourself and your vehicle. Remember, charging takes longer than refuelling, so plan for extra time in your itinerary.
Before you head out, charge your EV overnight. If you don’t have a private charger, look for on-street options nearby.
Use your GPS to explore different route options; while motorways are faster, A roads can help extend your EV’s range.
Make the most of charging stops by saving your favourite locations and consider scenic breaks to enjoy a meal or coffee.
MUST-DO CHECKS BEFORE YOU HIT THE ROAD WITH YOUR EV
NO DRIVEWAY CHARGER?
 CHECK OUT THIS BP PULSE GUIDE FOR TIPS ON CHARGING YOUR EV.
CHECK OUT THIS BP PULSE GUIDE FOR TIPS ON CHARGING YOUR EV.
Planning an EV road trip can be simple and stress-free with a little preparation. Beyond google maps, use EV-specific apps like Zap-Map, Osprey or Fastned to find any of the 57,290 charging points across the UK.

RANGE ANXIETY
HOW TO OVERCOME IT
KNOW YOUR EV'S RANGE
Understand your vehicle’s real-world range, considering factors like driving habits and terrain.
INCORPORATE ECO-DRIVING
Drive smoothly, avoid rapid acceleration, and use regenerative braking to extend your range.
CONSIDER WEATHER IMPACT
Cold or hot weather can reduce range, so plan more frequent charging stops during extreme weather conditions.
CHARGE AT HOME REGULARLY
Start each day with a full charge by charging overnight, if possible.
MONITOR BATTERY USAGE
Keep an eye on your battery level and adjust driving behaviour to conserve energy.
CHARGE WHEN YOU STOP
Plan to charge during natural breaks, like meals, rather than stopping specifically to charge.
PLAN STOPS AT
LESS BUSY CHARGERS
Avoid congested motorway chargers by stopping at less busy stations slightly off main routes
USE ROUTE
PLANNING APPS
Apps like Zap-Map, Osprey, and Fastned can help you find charging stations along your route.
USE FAST CHARGERS
FOR LONG TRIPS
On longer journeys, stop at fast chargers to recharge quickly.
PLAN BACKUP
CHARGING STOPS
Have alternate charging stations in mind in case your first option isn’t available.
Choose charging points with multiple chargers and reliable networks to minimize wait times and ensure availability.
CHARGING
YOUR EV
EXPLORE YOUR OPTIONS
TYPES OF EV CHARGERS:
EV charging is categorized into three levels based on power output and charging speed:
LEVEL 1 CHARGER:
Using a standard household outlet (max 2.3 kw), this charger provides about 4-5 miles of range per hour, making it the slowest option and best suited for overnight charging.
LEVEL 2 CHARGER:
Common in homes, public parking, and commercial locations, level 2 chargers deliver between 3.4 kw and 22 kw. They can provide up to 75 miles of range in an hour, making them a popular choice for faster charging.
LEVEL 3 CHARGER
(DC FAST CHARGER):
These chargers offer the quickest charging times by delivering direct current (dc) power directly to the battery. Ideal for service stations, they allow for rapid charging in minutes, greatly reducing downtime for EV drivers.

WANT TO LEARN MORE? CLICK HERE FOR EVBOX’S CAR CHARGING GUIDE
THE TOP FIVE CHARGING LOCATIONS IN THE UK
AC (ALTERNATING CURRENT)
DC (DIRECT CURRENT)
Electric current that periodically reverses direction, making it suitable for charging electric vehicles (EVs) at home and public stations, as it can easily be converted to power various devices
Electric current that flows in a single direction, providing a steady voltage that is essential for fast charging stations, enabling quicker battery replenishment for EVs during long journeys.
CHARGING TIME AND COSTING
Charging an electric vehicle varies in time and cost based on battery size, charging method, and electricity rates. DC fast charging is quicker, while ac home charging takes longer. Generally, home charging is more economical than public options.
Whether you’re charging at home or using a public network, check out zap map’s handy tool for an easy way to calculate charging times and costs
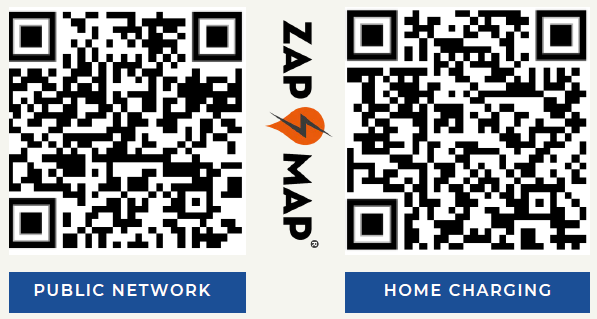
Public Network: https://www.zap-map.com/tools/public-charging-calculator
Home Charging: https://www.zap-map.com/tools/home-charging-calculator
WHAT WILL AFFECT
YOUR RANGE?
To maximize your EV’s range, adopt strategies that enhance efficiency, such as mindful driving, optimizing charging practices, and proper vehicle maintenance. These techniques can help you extend your EV’s range and get the most out of each charge.

USE OF CLIMATE CONTROL
Air conditioning or heating draws power from the battery.

TEMPERATURE
Extreme cold can reduce battery efficiency, while extreme heat may necessitate more energy for cooling.

OPEN WINDOWS
When windows are open, it disrupts the vehicle’s aerodynamic profile, increasing air resistance (drag).

TYRE PRESSURE
Under-inflated tyres create more rolling resistance, lowering efficiency.

ROAD CONDITIONS
Poor or unpaved roads may increase energy consumption.

SPEED
Driving at higher speeds increases aerodynamic drag and energy consumption.

DRIVING STYLE
Aggressive driving, such as rapid acceleration and hard braking, can reduce range.

DRIVING MODE
Different modes (ECO vs. Sport) can influence efficiency.

WEIGHT
Carrying heavy loads or more passengers can decrease range.

TERRAIN
Hilly or mountainous areas require more energy than flat terrain.
WHAT WILL NOT
AFFECT
YOUR RANGE?

Some features in electric vehicles have only a minor impact on range, allowing for added comfort without significantly affecting battery life.
This means you can enjoy these enhancements while still maintaining efficient driving.









